The serial interface is mainly used for serial bit-by-bit data transmission. As long as a pair of transmission lines can realize two-way communication, it has the advantages of simple communication line and low cost. Many serial data interfaces are now used in specific areas, such as I2C, CAN, LIN, SPI, Flex, MOST, and I2S. Of course, there are also interfaces with higher transfer rates, such as FireWire, HDMI, and Thunderbolt. But today we have to say that the serial interface can be called the originator of these interfaces, they are -- RS-232 and RS-485. Due to the earliest appearance, many people think that these two interfaces are outdated or discontinued. But in fact, they are still active in the field of data transmission and continue to play their light and heat. The following two types of interface types will be analyzed one by one.
RS-232
In 1970, the RS-232 interface was introduced. It is the world's first serial interface and can only support one-to-one transmission. Initially, it was used as a method for connecting data terminal equipment (DTE), often connecting video terminals, computers and modems. When the RS-232 interface first appears on a personal computer, it is called a serial port and is used to connect to a printer or other device. Today, it is still widely used in embedded computer development systems, scientific instruments, and various industrial control devices.
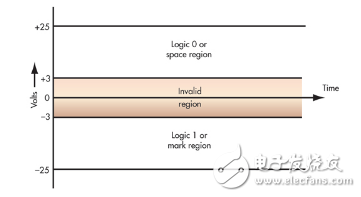
The RS-232 standard specifies that the level of logic one is between -3 V and -25 V, while the level of logic zero is between +3 V and +25 V, and its level close to zero is invalid (see figure one). The logic one is defined as a negative level, the signal state of the effective negative level is called mark marking, its function meaning is OFF; the logic zero is defined as positive level, and the signal state of the effective positive level is called empty spacing, its function The meaning is ON. Normally, the logic one and logic zero minimum voltages fluctuate between ±5 V, with the highest voltage typically between ±12 V or ±15 V.
There are two types of cable media that connect to the RS-232 interface - parallel or twisted pairs. The length of the cable should generally not exceed 15m in order to limit the maximum transmission rate of data. However, the cable length can be longer than 15 m when applied to a very low data transfer rate. When connecting cables for transmission, the capacitance between the cables should be limited to 2500 pF, so that the data rate can be controlled at around 20 kbits/s. However, since the data transmission rate is low and there is no matching generator and load impedance to mitigate the attenuation of the data, the connected cable is usually not considered a regular transmission line.
In addition, RS-232 also specifies 20 different signal connections, DB-25 connectors consisting of 25 D-sub (mini-D) pins. However, due to the saving of money and space, this connector is now rarely used, and it is replaced by a 9-pin D-sub or a DB-9 connector. The control signals used on a typical nine-pin connector are as follows:
Data Carrier Detection (DCD): The DCE side informs the DTE that it is receiving a valid signal.
Data Ready (DSR): The DCE side informs the DTE that it is ready to receive signals.
Accept Data (RD): The actual signal received from the DTE.
Request to Send (RTS): The signal at the DTE side tells the DCE that it is ready to transmit.
Transmit Data (TD): A signal sent from the DTE side.
Clear to Send (CTS): The DCE side informs the DTE that it is ready to receive data.
Data Terminal Preparation (DTR): Indicates that data is ready to be transmitted or received from the DTE side to the DCE side.
Ringing indication (RI): This line is used in the old modem connection, but is no longer used.
Common ground: All signal ground connections.
RS-485
RS-485, now commonly referred to as TIA-485, enables point-to-point connections and connection between one-to-many points. Compared to RS-232, all aspects of RS-485 are extended: its data transfer rate is higher, the interface allows up to 128 transceivers to be connected on the bus, and it also has the capability of two-way communication. This standard specifies that the level of logic one must not be lower than –200 mV and the level of logic zero must not be lower than +200 mV. It is effective when the voltage difference between the two ends is at least 0.2V, but the network can work normally as long as the voltage range is between -7 and +12V.
The RS-485 standard transmission medium is a #22 or #24 AWG solid-core twisted pair cable. If full-duplex operation is required, a four-wire twisted pair cable is required. It can transmit high voltage differential balance through twisted pair, and the maximum transmission distance can exceed 1200m. Ideally, EIA-485 requires two termination resistors whose resistance requirements are equal to the characteristic impedance of the transmission cable to prevent errors in data transmission. In many cases, when connecting an RS-485 communication link, simply connect the "A" and "B" ends of each interface with a pair of twisted pairs. The RS485 interface connector adopts the DB-9 9-pin connector. The RS485 interface with the intelligent terminal adopts DB-9 (hole), and the keyboard interface RS485 with keyboard is DB-9 (pin).
Application field
RS-232 is now generally used in short-distance transmission with low data transmission rate, and can work effectively in noisy environments, such as factories, public stations, etc. Its common equipment includes low-speed modems, industrial control equipment, and programmable logic controllers. PLC), computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools, robots, embedded control computers, medical instruments and equipment, and embedded controller development systems. RS-485 is often used for long-distance transmission with high data transmission rates. Commonly used equipment includes point-of-sale terminals (POS), measuring instruments, and large-scale dedicated automation machines.
But in normal applications, we often need to convert between two different interface types. At this time we can use the popular USB interface, which can help us switch to RS-232 interface and RS-485 interface.
In summary, RS-232 is suitable for short-distance low-rate transmission requirements, while RS-485 is suitable for long-distance transmission. RS-485 is a new interface standard for the lack of RS-232 interface. It has become the preferred standard because of its good anti-noise ability and multi-station capability.
Pcb Pluggable Terminal Block Connector ,Pluggable Terminal Block,Contact Pluggable Terminal Blocks ,Pluggable Screw Terminal
Cixi Xinke Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cxxinke.com