This article refers to the address: http://
For PCB layout engineers, today's mobile phones pose the ultimate challenge. Modern mobile phones contain almost all subsystems found in portable devices, such as multiple RF modules (including cellular, short-range wireless transmission); audio, video subsystems; dedicated application processors, and The increased I/O layout is required for application requirements, and each subsystem has conflicting requirements.To integrate so many complex subsystems in such a small space, the reality to be considered is all-encompassing. In addition to the possible interference between the RF subsystems, different subsystems may be operated by themselves or by wiring. Mutual interference, EMI problems, etc., test the professional capabilities of mobile phone PCB engineers.
A well-designed board must be able to maximize the performance of each component mounted on it and avoid interference between different systems. Because if there is a conflict between the subsystems, the result will inevitably lead to a decline in performance.
Today, despite the ever-increasing audio functionality in mobile phones, much attention has been focused on the RF subsystem in circuit board design, and audio circuits have received the least attention. However, audio quality, especially with high-fidelity sound quality, has become one of the key points affecting whether a high-end mobile phone can be quickly accepted by the market. This article provides some suggestions to help ensure a board that is well laid out without sacrificing audio quality.
Recommended practice
* Careful consideration of layout planning. The ideal layout plan should divide the different types of circuits into different areas to minimize interference. The picture above shows a good layout plan.
* Use differential signals whenever possible. Audio components with differential inputs can suppress noise.
* Isolate the ground current to prevent the digital current from increasing the noise of the analog circuit.
* The analog circuit uses a star ground. The current consumption of audio power amplifiers is usually large, which can have an adverse effect on their own ground or other reference ground.
* Turn unused areas on the board into ground planes. A ground flood is performed near the signal trace, and unwanted high frequency energy in the signal line can be capacitively coupled to the ground.
Not recommended practice
* Use a hybrid circuit on the board. Although the RF area of ​​a cell phone is generally considered analog, noise coupled from the RF zone to the audio circuitry may be demodulated into audible noise.
* The analog audio signal wiring on the board is too long. Too long analog audio traces can absorb noise from digital and RF circuits.
* Forget the importance of the ground loop. Systems with poor grounding are likely to experience severe distortion, noise, crosstalk, and low RF immunity.
* The natural loop that interrupts the digital current. This path has the smallest loop area to minimize the effects of antenna and sensing.
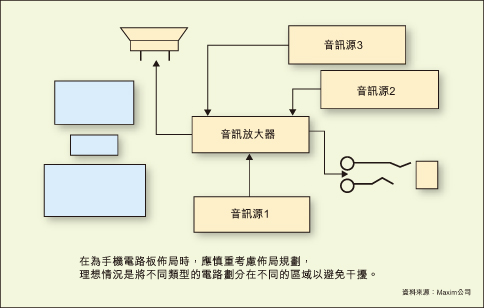
Figure: * When laying out a mobile phone board layout, layout planning should be carefully considered. Ideally, different types of circuits should be divided into different areas to avoid interference.
Carbon Steel Plate Mill,Automatic Cold Rolling Mill,Reversible Cold Rolling Mill,Cold Rolling Mill
Haoshuo Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.whrollformingmachine.com