0 Preface
With the development of China's economic construction, especially the construction of the country's 7918 road network, road construction, especially highway construction, has developed rapidly. Among them, road tunnels have been widely used in mountain road construction due to their advantages of shortening mileage, saving time, improving transportation efficiency, saving land and protecting ecological environment. Many long tunnels have been built, such as Yanmenguan Tunnel and Xuefeng Mountain. The tunnel is the first in the world and the second in the world, the Qinling Zhongnanshan Tunnel. At the same time, the scale and number of tunnel lighting and ventilation facilities are also increasing, and the operating and maintenance costs are also increasing. Since tunnels generally require 24 hours of uninterrupted lighting, the energy consumption of tunnel lighting is as high as 40% to 50% of the total operating energy consumption. Therefore, how to save tunnel lighting energy consumption is receiving more and more attention from the government and people. Lighting energy saving is an important research direction in tunnel lighting design.
Although there are relevant energy-saving standards and measures for urban road lighting design in China, there are only relevant design codes and standards for highway tunnel lighting design, and there is no provision for tunnel lighting energy-saving standards. Tunnel lighting is very different from urban road lighting because of its own characteristics. It is not possible to directly apply and reference road lighting energy-saving standards and specifications. Therefore, how to determine reasonable tunnel lighting energy-saving standards is an urgent task to be solved in current tunnel lighting energy conservation.
1 The role and significance of tunnel lighting power density
Lighting energy conservation is an important part of energy conservation in the whole society. Green lighting is one of the top ten energy-saving topics in China's medium and long-term development planning. In order to implement the guiding ideology and purpose of national green lighting, since 2004, various departments have formulated and revised a series of lighting design standards, all of which have new regulations on lighting energy-saving standards, such as the national standard issued in 2004. Architectural lighting design standards 6, the industry standard 5 urban road lighting design standards released in 2006 and the local standards issued by Chongqing in 2006 5 Chongqing city night lighting technical specifications 6 and so on. In these standards, the concept of lighting energy efficiency (LPD) has been officially defined for the first time.
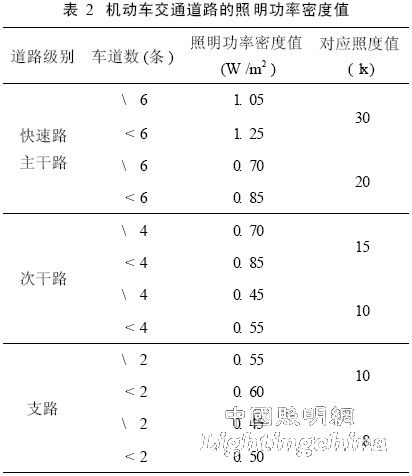
Lighting Power Density is the lighting installation power per unit area (including light source, ballast or transformer). It comprehensively considers the power loss of the entire lighting system, and is more comprehensive and scientific in terms of energy saving effect. At the same time, LPD is a relatively simple and easy to operate indicator, which is convenient for designers to implement and facilitate the management department to evaluate the energy saving effect. . Therefore, in the above-mentioned standards, LPD is used as an evaluation index of lighting energy saving (as shown in Table 1 and Table 2), and these LPD values ​​(except residential buildings) are issued as compulsory provisions, that is, requirements Must be strictly enforced.
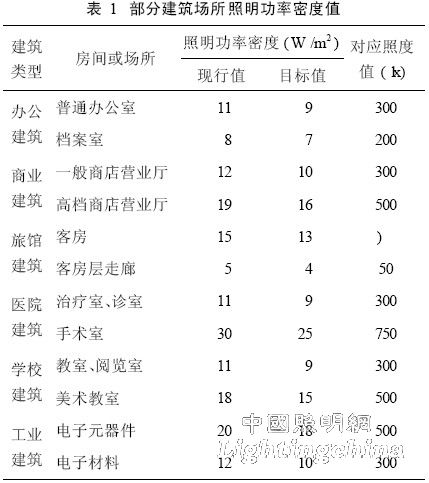
The LPD value specified in the standard refers to the maximum allowable value of the LPD, that is, the energy saving effect is achieved by limiting the LPD value under the condition of ensuring the corresponding lighting quality. This evaluation index has played a huge role in promoting the energy saving of architectural lighting, and truly reduced the energy consumption of lighting into a quantitative way.
Regrettably, the current 5 road tunnel ventilation lighting design specification 6 is an industry standard issued in 1999. At that time, the requirements for tunnel lighting energy-saving standards were not fully considered, which led to the lack of energy-saving quantification in tunnel lighting design. The evaluation indicators have caused great difficulties in the development and implementation of tunnel lighting energy conservation work. Therefore, the development of tunnel lighting energy-saving standards is an urgent task in tunnel lighting engineering.
Referring to the experience of developing and revising lighting standards at home and abroad in recent years, the author believes that LPD can also be used as an evaluation index for tunnel lighting energy conservation when developing tunnel lighting energy-saving standards. Therefore, how to determine a reasonable tunnel LPD value becomes a key issue in the development of tunnel lighting energy-saving standards.
In summary, the study of LPD values ​​in tunnel lighting is an important way to develop energy-saving standards for tunnel lighting and to achieve energy-saving for tunnel lighting. The research results play an important role in the implementation of tunnel lighting energy conservation and the promotion of energy-saving technologies. It is more practical to alleviate the shortage of power supply, reduce the operating cost of tunnels, and build a conservation-oriented society.