In today's digital landscape, most organizations recognize that the data they collect daily is a vital asset that fuels their business operations. It’s not just about meeting legal or compliance requirements—it's about unlocking valuable insights that lead to smarter decisions, improved processes, and greater profitability. To realize this potential, data must be accessible in real time while maintaining high levels of security and availability.
As users increasingly connect to data centers through mobile devices, the demand for seamless access to information has grown. The internet is now more widespread than ever, and with it comes an explosion of data from photos, videos, social media, and streaming services. While traditional devices like desktops, laptops, smartphones, and tablets still generate massive amounts of data, the future will see even more coming from autonomous vehicles, industrial robots, sensors, drones, and medical devices. This shift has driven the need for scalable cloud-based data centers and advanced storage solutions.

Storage systems rely on a variety of devices such as SSDs, HDDs, and tapes to handle growing data volumes. SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) is a powerful solution for ensuring fast, reliable, and secure data transfer across enterprise environments. As a point-to-point interconnect protocol, SAS offers faster throughput compared to older parallel technologies, supports multipath I/O, and provides a robust and well-defined infrastructure. These features make SAS ideal for mission-critical applications where performance and reliability are essential.
Despite some speculation, SAS remains a strong choice for enterprise storage. Leading manufacturers continue to invest in flash-based SAS SSDs due to their unique advantages over other protocols. SAS isn’t going away anytime soon—its reliability and performance make it a cornerstone of modern data center infrastructure.
SAS Overview
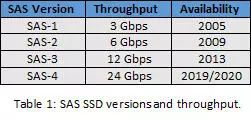
SAS is a serial storage interface built upon the legacy parallel SCSI protocol, which was widely used in the 1980s. Today, it’s the standard for enterprise storage solutions. As shown in Table 1, SAS development has been driven by the need to move larger volumes of data efficiently. The next generation of SAS will maintain backward compatibility with previous versions, ensuring smooth transitions for existing systems.
The SAS interface is maintained by the T10 Technical Committee under the INCITS standards organization. This ensures consistent development and broad industry adoption.
Key Advantages of SAS
SAS connects HBAs or RAID controllers to enterprise-grade SSDs or HDDs, enabling efficient data management and protection. RAID technology allows for data mirroring or distribution across multiple drives, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. If a drive fails, a hot-swappable replacement can be inserted without downtime, and the RAID controller rebuilds the data using parity information. This level of reliability is crucial for IT teams managing critical infrastructure.

A single SAS HBA card can support up to 24 drives, combining SSDs and HDDs for optimal performance and capacity. SAS RAID cards offer similar flexibility, allowing for enhanced performance and data protection. This hybrid approach helps data centers maximize storage efficiency and reduce costs.
SAS also supports high availability through dual-port functionality, offering two independent data paths for each drive. This means if one path fails, the other continues to operate seamlessly, minimizing service disruption. For configurations with large numbers of drives, such as JBOD setups, dual ports and RAID are essential for maintaining system stability. Currently, only SAS drives provide mature dual-port capabilities.
Hot swapping is another major benefit of SAS. If a drive fails, it can be replaced without shutting down the system, reducing downtime and improving operational continuity. Additionally, since both HDDs and SSDs use the same SAS interface, they can be easily integrated into the same storage system, offering greater flexibility in deployment.
Energy efficiency is another advantage of SAS-based storage. Some SAS SSDs offer power-saving modes that reduce energy consumption when full performance is not required. For example, Western Digital’s latest Ultrastar SS300 series includes options for 9W, 11W, and 14W power levels, allowing users to balance performance and power usage based on their needs.
Future of SAS
With the rise of 3D NAND flash technology, storage density is increasing significantly. Unlike 2D NAND, 3D NAND stacks memory cells vertically, allowing for higher capacities in the same physical space. For instance, U.2 SSDs using 2D NAND can reach up to 8TB, but 3D NAND enables capacities of 60TB or more. This advancement also improves performance by reducing interference between memory cells, leading to more reliable and efficient storage solutions.
Looking ahead, the industry is preparing to launch SAS Gen4, which will double the data throughput of current 12Gbps SAS to 24Gbps, expected around 2019–2020. This upgrade will be backward compatible with earlier generations, ensuring continued support for existing SAS SSD investments.
Conclusion
As data volumes continue to grow, IT departments face increasing challenges in managing and securing their infrastructure. Many companies are consolidating data centers to cut costs and improve efficiency while maintaining performance and security. SAS-based storage solutions offer clear, stable, and proven infrastructure that meets these demands. With its high bandwidth and enterprise-grade capabilities, SAS is set to remain a key player in data storage for the next decade and beyond.
Electrical Ceramics,Conductive Ceramics,Electrically Conductive Ceramics,Electro Ceramics
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com